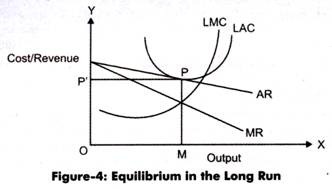
Figure-4 shows the long-run equilibrium position under monopolistic competition:
In Figure-4, P is the point at which AR curve touches the average cost curve (LAC) as a tangent. P is regarded as the equilibrium point at which the price level is MP (which is also equal to OF) and output is OM.
In the present case average cost is equal to average revenue that is MP. Therefore, in long run, the profit is normal. In the short run, equilibrium is attained when marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost. However, in the long run, both the conditions (MR=MC and AR=AC) must hold to attain equilibrium.