List of Medications
| Medication Name/
Frequency |
Indications | Actions | Contraindications | Side Effects | Nursing Implication |
| Apixaban (brand name- Eliquis) 5mg P.O. B.D.
|
§ Prevention of systemic embolism and stroke in non-valvular atrial fibrillation.
§ Treatment of pulmonary embolism. § Prevention of pulmonary embolism after knee or hip replacement surgery. § Treatment of deep venous thrombosis. § Prophylaxis of deep venous thrombosis after knee or hip replacement surgery. § Decreases the reoccurrence of pulmonary embolism and deep venous thrombosis (Agrawal et al., 2022).
|
§ Inhibits factor Xa, leading to blockage of the propagation phase in the coagulation cascade.
§ Inhibits thrombokinase activity and clot-bound and free factor Xa, leading to indirect inhibition of platelet aggregation caused by thrombin (Agrawal et al., 2022).
Therapeutic effects: § Prophylaxis and treatment of thromboembolic events. |
§ Hypersensitivity
§ Active bleeding § Patients with mitral stenosis, mechanical and prosthetic heart valves. § Forty-eight hours before invasive procedures or elective surgery with a moderate or high risk of bleeding § Twenty-four hours before invasive procedures or elective surgery, with a low risk of bleeding (Agrawal et al., 2022)
|
§ Hypersensitivity reaction (allergic edema, rashes)
§ Bleeding § Epistaxis § Rectal hemorrhage § Gingival hemorrhage § Postoperative hemorrhage § Nausea § Hematuria § Bruising § Hemoptysis § Increased levels of gamma-glutamyltransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and serum transaminases (Agrawal et al., 2022).
|
Assessment:
§ Administer oral-activated charcoal in case of an apixaban overdose. § Monitor the patient for pulmonary embolism and deep venous thrombosis during therapy with apixaban.
Implementation: § Discontinue apixaban 48 hours before invasive procedures or elective surgery with a moderate or high risk of bleeding. § Discontinue apixaban 24 hours before invasive procedures or elective surgery with a low risk of bleeding. § Warfarin should be replaced by apixaban when INR is less than 2. § Discontinue apixaban before initiating therapy with another anticoagulant, such as warfarin (Agrawal et al., 2022).
Patient/Family Teaching: § Advise patient to take apixaban as directed, even if feeling well. § Advise the patient to take a missed dose as soon as possible on the same day. § Educate the patient on signs of bleeding and other side effects. § Advise the patient to take a missed dose as soon as possible on the same day. § Advise the patient to resume taking medication twice daily after a missed dose. § Advise the patient against doubling the dose when there is a missed dose. § If the patient cannot swallow, advise the patient to crush the tablet and suspend it in water (Agrawal et al., 2022). § Advise the patient to take the medication with or without food. § Advise patients to disclose their medication history if they visit a different healthcare provider. § Advise the patient to look for signs of hypersensitivity, such as rashes. § Advise patient against taking over-the-counter medications and herbal medications. |
| Amiodarone 600mg B.D. P.O. for three weeks, followed by 300mg B.D. P.O. for one month, followed by a maintenance dose of 400mg O.D.
|
§ Pulseless ventricular tachycardia/ ventricular fibrillation.
§ Ventricular arrhythmias. § Stable monomorphic ventricular tachycardia. § Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (Florek & Girzadas, 2022).
|
§ Inhibits adrenergic stimulation, leads to repolarization, prolonged action potential, decreased sinus node function, and atrioventricular conduction (Florek & Girzadas, 2022).
Therapeutic effect: § Management of ventricular arrhythmias.
|
§ Hypersensitivity
§ Cardiogenic shock § Bradycardia with syncope. § Marked sinus bradycardia. Second-degree atrioventricular block (Florek & Girzadas, 2022). § Third-degree atrioventricular block.
|
§ Hypotension
§ Altered memory § Hypothyroidism § Increased levels of aspartate aminotransferase and serum transaminases § Dizziness § Fatigue § Photosensitivity § Headache § Ataxia § Constipation § Sleep disturbances § Congestive heart failure § Hyperthyroidism § Sinoatrial node dysfunction § Bradycardia Hepatitis (Florek & Girzadas, 2022). |
Assessment:
§ Monitor the patient’s heart rate and blood pressure (Florek & Girzadas, 2022).
Patient/Family Teaching: § Advise patient to take amiodarone as directed, even if feeling well.
|
| Atorvastatin 2mg P.O. O.D. nocte | § Prophylaxis or decreased risk of stroke and myocardial infarction.
§ Management of hypercholesterolemia, dyslipidemia, and hypertriglyceridemia (McIver & Siddique, 2022). |
§ Inhibits HMG-CoA reductase, decreasing cholesterol synthesis (McIver & Siddique, 2022).
Therapeutic effect: § Prophylaxis of stroke.
|
§ Hypersensitivity
§ Pregnancy § Lactation § Liver disease § Unexplained elevated transaminase (McIver & Siddique, 2022).
|
§ Diarrhea
§ Arthralgia § Nasopharyngitis § Urinary tract infection § Insomnia § Myalgia § Dyspepsia (McIver & Siddique, 2022). |
Assessment:
§ Monitor the patient’s weight and BMI. § Monitor the patient’s liver function. § Monitor the patient’s serum lipid levels and HbA1c.
Patient/Family Teaching: § Advise the patient to take atorvastatin as directed, even if feeling well. § Advise the patient on dietary modifications and lifestyle modifications to control hypercholeste § Advise the patient to take atorvastatin at night before bedtime (McIver & Siddique, 2022). |
Labs and Diagnostic Tests:
| Labs And Diagnostic Test/Labs | Purpose/ Indications | Normal Values | Client Result | Interpretation of Abnormal Results |
| RBC
|
– To determine blood-related conditions. | 3.8 to 5.2 million/mm3 | 3.35 million/mm3 | Decreased levels may indicate:
– Internal bleeding. – Vitamin B6 deficiency – Vitamin B12 deficiency – Folate deficiency |
| HGB | – To determine blood-related conditions. | 11.6 to 15 grams/decilitre | 10.5 grams/decilitre | Decreased levels may indicate:
– Internal bleeding. – Vitamin B6 deficiency – Vitamin B12 deficiency – Folate deficiency |
| RDW
|
– To detect blood-related conditions and anemia.
|
12 to 15% | 16.8% | Increased levels may indicate:
– Anemia – Internal bleeding |
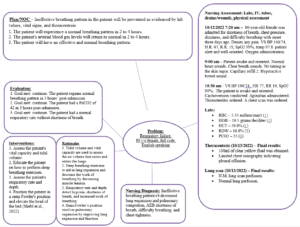
Nursing Diagnosis Two
Hypertension
Nursing Interventions
Monitor blood pressure and response to medications.
Relacation techniques.
Dietary adjustments, including cholesterol restrictions.
Nursing Rationales
Monitor blood pressure and response to medications to adjust drug dosage.
Relaxation techniques to decrease stress, encourage calmness, and lower blood pressure.
Dietary adjustments, including cholesterol restrictions, to decrease myocardial workload (Iqbal & Jamal, 2022).
Nursing Diagnosis Three
Acute bronchitis
Nursing Interventions
Assess the airway for obstructions.
Chest auscultation.
Position the patient’s bed at 30 degrees.
Nursing Rationales
Assess the airway for obstructions to ensure an efficient gas exchange process.
Conduct chest auscultation to rule out airway obstruction.
Position the bed at 30 degrees to elevate the patient’s breathing pattern and allow normal lung expansion (Singh et al., 2022).
References
Agrawal, A., Kerndt, C. C., & Manna, B. (2022). Apixaban. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507910/.
Florek, J. B., & Girzadas, D. (2022). Amiodarone. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482154/.
Iqbal, A. M., & Jamal, S. F. (2022). Essential Hypertension. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539859/.
McIver, L. A., & Siddique, M. S. (2022). Atorvastatin. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430779/.
Nesheiwat, Z., Goyal, A., & Jagtap, M. (2022). Atrial Fibrillation. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526072/.
Shebl, E., Mirabile, V. S., Sankari, A., et al. (2022). Respiratory Failure. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526127/.
Singh, A., Avula, A., & Zahn, E. (2022). Acute Bronchitis. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448067/.
ORDER A PLAGIARISM-FREE PAPER HERE
We’ll write everything from scratch
Question 

Fundamentals of Nursing Care Plan
Present History: Admitting Medical Diagnosis:
Why the client is in the hospital:
Medical diagnosis (does not include signs and symptoms)
Admitting Diagnosis Information:
This paragraph should describe the signs and symptoms that caused the patient to visit the hospital. It should not be what the doctor writes word for word. Paraphrase into your words. You may quote the patient.
Definition/Etiology/Pathophysiology:
This paragraph is to define and explain the admitting diagnosis/disease.
This paragraph should describe the etiology. The etiology is what causes the disease.
This paragraph should explain the pathophysiology of the patient’s disease. Pathophysiology describes what the disease does to the body.
Clinical Manifestations/Signs and Symptoms:
This/these paragraphs should explain what the textbook manifestations are and whether the signs and symptoms of the patient are similar or different.
Medical Management:
This/these paragraphs should explain the textbook medical management for the admitting diagnosis of disease. What medical management is currently being done for the patient?
Past History/Secondary Diagnosis:
Name an additional diagnosis that the patient has.
Definition/Etiology/Pathophysiology:
Complete definition/etiology and pathophysiology for the secondary diagnosis as above.
Clinical Manifestations/Signs and Symptoms:
Complete clinical manifestations and signs and symptoms for secondary diagnosis as above.
Medical Management
Complete the medical management of the secondary diagnosis as completed above.