A comparative analysis of monopoly and monopolistic competition has been made on the following aspects:
1. Nature of Product:
Under monopoly, product produced may or may not be homogeneous. But under monopolistic competition, there is always product differentiation.
2. Number of Buyers and Sellers:
Under monopoly, there are many buyers but only one seller. On the other hand, under monopolistic competition, there are close substitutes for the product, so there are many sellers of a product.
3. Entry and Exit:
Under monopoly, there are strong barriers on the entry of new firms. On the other hand, under monopolistic competition, new firms can enter into the market and same can exit the market. But it is possible only in the long run not in the short run.
4. Degree of Knowledge:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Under monopoly, we assume that the sellers and buyers have complete knowledge regarding market activities. But under monopolistic competition, there is imperfect knowledge on the part of buyers and sellers.
5. Revenue Curves:
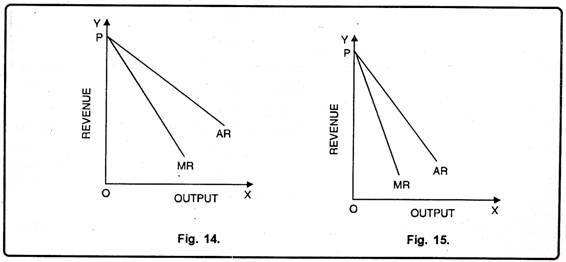
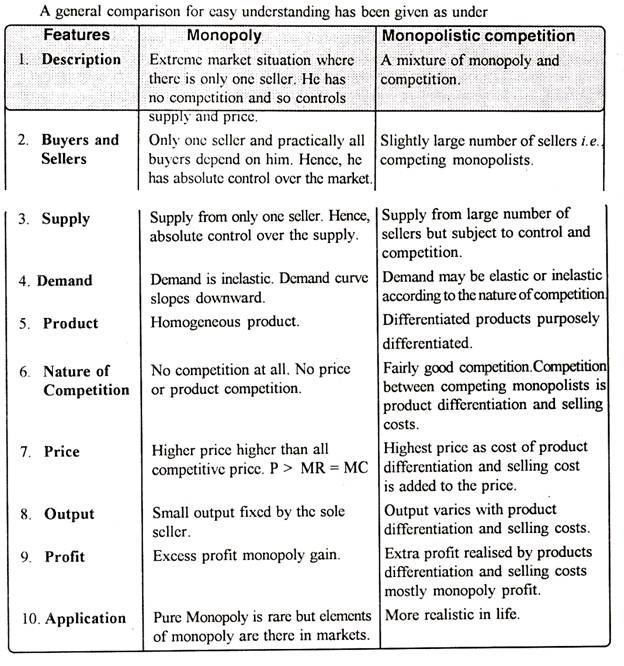
Under monopoly, AR and MR are different. AR refers to price, MR refers to marginal revenue. These curves are less elastic. It means for a small increase in sales (demand), the monopolist has to reduce the price to greater extent. It means revenue curves are less elastic. Fig. 15 shows less elastic AR and MR. Under monopolistic competition also, the revenue curves are different but in this case, the revenue curves are more elastic. It means small fall in price, will lead to big increase in demand. Fig. 14 represents AR and MR under monopolistic competition.
6. Decision-Making:
Under monopoly and monopolistic competition, a firm cannot determine both price and output at the same time. Under monopolistic competition, the firm has to spend more on selling costs. On the other hand, under monopoly the firm has to spend a small amount on selling costs.
7. Nature of Profits:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In the short run, both under monopoly and monopolistic competition, the firm can enjoy super-normal profits, normal profits or can sustain losses. But in the long run, firm under monopolistic competition will enjoy only normal profits.
Advantages of Monopolistic Competition:
Regarding the advantages of monopolistic competition, the issue can be analyzed on many fronts.
A brief description is as under:
1. Economic Point of View:
From the economic side, it might be argued that selling expenses increase the velocity of circulation of money and so increase employment. Here, it has been pointed out that there are cheaper and more dignified ways of increasing employment and this argument breaks down completely in a time of full employment, and still more in a time of inflation.
2. Sociological Point of View:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
On the sociological side, it might be argued that advertising has itself an entertainment and cultural value, and that it promotes mass communication in the form of cheaper magazines, news papers, radio and television. Prof. Boulding has doubted upon the significance of this value also. Thus, he said, “I am happy to leave this argument to the sociologists.”
3. On the Basis of Monotony:
Much controversy and honest doubt surrounded these issues. Some economists think that the wastes due to monopolistic competition are, in-fact, small. Others argue that product differentiation satisfies consumer’s desires for variety and breadth of choice if pure competition prevails everywhere, homogeneity of products would mean lower costs. Would not life then be dull? If the whole population were put into uniform clothes and made to live in uniform barracks, vast quantities of resources would be released, but what for?